MCUs and FPGAs
We have several microcontroller units (MCU) and field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) for students to use.
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a configurable integrated circuit that can be programmed using an HDL (Hardware Description Language). FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of a grid-connected array of programmable logic blocks that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. The logic blocks of an FPGA can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more sophisticated blocks of memory.[1] Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigurable computing as performed in computer software.
Microcontroller Kits


DuinoKit allows you to program with an Arduino microprocessor.
DuinoKit Educator
Component List: Arduino NANO compatible microprocessor, ADXL345 Acceleration Sensor, Ultrasonic Distance Sensor, Auto-Off Module, IR Remote Controller, PS2 Joystick Module, Relay, Stepper Motor, ULN2003-based Stepper Motor Driver, DHT-11 Temperature & Humidity Sensor, LED Bar Graph Array, Active Buzzer, Passive Buzzer, Servo, Analog Temperature Sensor(Thermistor), Power Supply Module, 4*4 Matrix Keyboard, DC Motor, L9110 Motor Driver, LCD1602, 8x8 Dot-matrix LED Display, 8 digits 7-segment Display with Shift Register, 7-segment LED Display, Light Sensor(Photoresistor), Tilt Switch, Switches, RGB LED, Red LEDs, Green LED, Yellow LED, Blue LEDs, Resistors(220Ω), Resistors(1KΩ), Resistors(10KΩ), Potentiometers(10KΩ), Capacitors(104), Capacitors(10uF), Buttons, NPN Transistors(8050), PNP Transistors(8550), 1N4148 Diodes, 1N4001 Diodes, Battery Holder, Breadboard, USB Cable, Male to Male Jumper Wires, Male to Female Jumper Wires, Band Resistor Card, Rotary Encoder, oLed 64x128 module, IRF520 Mosfet transistor, TSOP4838 IR receiver module, 8 digits, 7 segment display module with MAX7221 driver, 8x8 LED array with MAX7221 driver, DS1307 Real Time Clock Module, 2N2222 Transistor, 2N2907 Transistor, 10 WS2812B LED Strip
DuinoKit IoT
Component List: Arduino compatible ESP32 microprocessor, GPS module, Passive Infared Motion Sensor (PIR), ADXL345 Acceleration Sensor, Ultrasonic Distance Sensor, Auto-Off Module, IR Remote Controller, PS2 Joystick Module, Relay, Stepper Motor, ULN2003-based Stepper Motor Driver, DHT-11 Temperature & Humidity Sensor, LED Bar Graph Array, Active Buzzer, Passive Buzzer, Servo, Analog Temperature Sensor(Thermistor), Power Supply Module, 4*4 Matrix Keyboard, DC Motor, L9110 Motor Driver, LCD1602, 8x8 Dot-matrix LED Display, 8 digits 7-segment Display with Shift Register, 7-segment LED Display, Light Sensor(Photoresistor), Tilt Switch, Switches, RGB LED, Red LEDs, Green LED, Yellow LED, Blue LEDs, Resistors(220Ω), Resistors(1KΩ), Resistors(10KΩ), Potentiometers(10KΩ), Capacitors(104), Capacitors(10uF), Buttons, NPN Transistors(8050), PNP Transistors(8550), 1N4148 Diodes, 1N4001 Diodes, Battery Holder, Breadboard, USB Cable, Male to Male Jumper Wires, Male to Female Jumper Wires, Band Resistor Card, Rotary Encoder, oLed 64x128 module, IRF520 Mosfet transistor, TSOP4838 IR receiver module, 8 digits, 7 segment display module with MAX7221 driver, 8x8 LED array with MAX7221 driver, DS1307 Real Time Clock Module, 2N2222 Transistor, 2N2907 Transistor, 10 WS2812B LED Strip
(You will need your own Mac / PC / or Linux based computer for uploading the programs to the Arduino compatible processor.)
Online course tutorials and lessons Moodle Classroom server (TinkerCode.us) Course materials and component lessons are available to individuals and private classrooms with teacher access can be created for groups with lesson assessments.
Microcontrollers
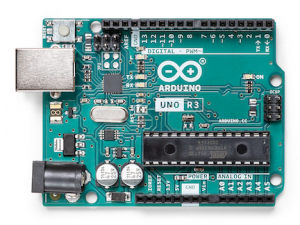
Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz ceramic resonator (CSTCE16M0V53-R0), a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.. You can tinker with your Uno without worrying too much about doing something wrong, worst case scenario you can replace the chip for a few dollars and start over again.
"Uno" means one in Italian and was chosen to mark the release of Arduino Software (IDE) 1.0. The Uno board and version 1.0 of Arduino Software (IDE) were the reference versions of Arduino, now evolved to newer releases. The Uno board is the first in a series of USB Arduino boards, and the reference model for the Arduino platform; for an extensive list of current, past or outdated boards see the Arduino index of boards.
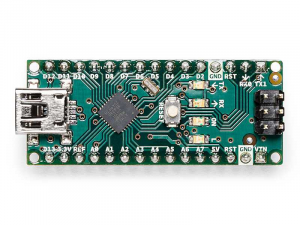
The Arduino Nano is a small, complete, and breadboard-friendly board based on the ATmega328 (Arduino Nano 3.x). It has more or less the same functionality of the Arduino Duemilanove, but in a different package. It lacks only a DC power jack, and works with a Mini-B USB cable instead of a standard one.
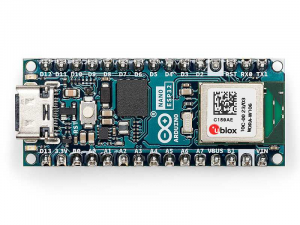
The Nano ESP32, a powerful addition to the Arduino ecosystem that brings the popular ESP32-S3 to the world of Arduino and MicroPython programming. Whether you're a beginner stepping into the world of IoT or MicroPython, or an advanced user looking to incorporate it into your next product, the Nano ESP32 is the perfect choice. It covers all your needs to kick-start your IoT or MicroPython project with ease.
Tiny footprint: Designed with the well-known Nano form factor in mind, this board's compact size makes it perfect for embedding in standalone projects.
- Wi-Fi® and Bluetooth®: Harness the power of the ESP32-S3 microcontroller, well-known in the IoT realm, with full Arduino support for wireless and Bluetooth® connectivity.
- Arduino and MicroPython support: Seamlessly switch between Arduino and MicroPython programming with a few simple steps. We even offer an introductory course for those new to the MicroPython world, find more information in the documentation page.
- Arduino IoT Cloud compatible: Quickly and easily create IoT projects with just a few lines of code. Our setup takes care of security, allowing you to monitor and control your project from anywhere using the Arduino IoT Cloud app. (Available starting August 2023)
- HID support: Emulate human interface devices, such as keyboards or mice, over USB, opening up new possibilities for interacting with your computer.
There are no more excuses to delay your exploration of IoT and MicroPython. The Nano ESP32 provides everything you need to start creating and discovering the endless possibilities.

The Teensy is a complete USB-based microcontroller development system, in a very small footprint, capable of implementing many types of projects. All programming is done via the USB port. The Teensy is available with header pins, for direct no-soldering-required use on a breadboard, which can also be run from the +5 volt from the USB cable. Standard Teensy boards come with solder pads. Either way, all Teensy boards come fully assembled and tested, so no surface mount soldering is needed.
Key Features:
- Compatible with Arduino Software & Libraries
- USB can be any type of device
- Single pushbutton programming
- Easy to use Teensy Loader application
- Free software development tools
- Works with Mac OS X, Linux & Windows
- Tiny size, perfect for many projects
- Available with pins for solderless breadboard
FPGAs
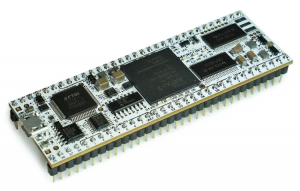
Micro-Nova Mercury 2 is a development board based around the Xilinx Artix 7 FPGA. The form factor of the board and the use of 5-volt tolerant IO pins make this board the preferred choice for FPGA development in the internship program. Dependency on proprietary Xilinx tools such as Vivado hamper its use but we are currently looking into using open source toolchains such as those implemented in the Alchitry Labs software.
Technical Specifications
- Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA (XC7A35T or XC7A100T)
- FTDI FT2232H 480Mbps USB 2.0 interface
- Channel A: device configuration and debugging (SPI Flash programming and USB-JTAG interface)
- Channel B: user-configurable interface between the FPGA and host for high-speed data transfer
- 50MHz MEMS oscillator (±50ppm)
- External Memory
- 32Mbit SPI configuration / user Flash
- 4Mbit (512K x 8-bit) or 16Mbit (2M x 8-bit) 10ns asynchronous SRAM
- Analog I/O
- Microchip MCP 3008 8-channel, 200 KSPS, 10-bit ADC
- Microchip MCP 4812 2-channel, 225 KHz, 10-bit DAC
- Artix-7 internal XADC 1MSPS , 12-bit ADC, accessible on dedicated ADC input or mappable to FPGA-direct IO
- Digital I/O
- 40x 5-volt tolerant IO pins provided by 2x TI SN74CB3T16210 bus switches
- 10x FPGA-direct high speed IO pins
- 3x User LEDs
- On-board Microchip LAN8720A 10/100 Ethernet PHY
- Expansion headers for Ethernet and Wi-Fi communication modules
- 6-pin header for direct JTAG interface to the Artix-7 FPGA
- Power
- Powered from Micro USB input or external 4.5 - 5.5V regulated power source
- On-board high-efficiency switching regulators for 3.3V, 1.8V and 1.0V rails

Alchitry Cu is a development board based around the Lattice iCE40 FPGA. The Cu features 79 IO pins at 3.3V. The signals for the on-board LEDs and reset button are also broken out giving you access to a maximum of 88 IO pins.
Open Source Tools The Lattice FPGA is supported by the official iceCube2 tools as well as unofficial open source toolchains.
USB C The USB C port on the board is used to configure the FPGA as well as transfer data to and from your design via a serial interface capable of up to 12M baud. This port can also supply the board its power and is protected by a diode if you decide to power the board externally.
Power The board is powered through the USB C port, 0.1” holes, or through its surface mount headers. The board requires 5V and generates 3.3V for IO and 1.2V for FPGA internal logic. The amount of current drawn is incredibly varied by your FPGA design but the power supply can pump out 3A on the 3.3V rail and 1.5A on the 1.2V rail so you don’t need to worry.
Peripherals Like all Alchitry boards, you get exactly what you need built into the board without all the extra fluff. The Cu has a 8 general use LEDs and a button typically used as a reset. It also has a 100MHz oscillator for clocking your designs. The FPGA is capable of synthesizing new frequencies from this if you need to clock your design faster or slower.
This device has been discontinued by the manufacturer in favor of the Cu V2

Alchitry Au is a development board based around the Xilinx Artix 7 FPGA.
Features
- XC7A35T-2FTG256I FPGA (speed and temperature grade upgrade over Au V1)
- 104 IO pins broken out across two headers
- 20 are triple voltage (3.3V, 2.5V, or 1.8V) of which 18 are LVDS_25 capable
- 44 pins are routed as 100 ohm differential pairs (includes 18 triple voltage pins)
- Remaining IO routed as 50 ohm single ended (~90 ohm when used as diff pairs)
- 2 1.35V pins on bank B
- 8 pairs can be used as inputs to the XADC (0-1V input range)
- Remaining IO is at 3.3V
- All pairs can be used as LVDS_25 inputs except three pairs on bank B
- Control Header
- 8 IO pins also connected to on-board LEDs
- 1 IO pin also connected to on-board reset button
- JTAG
- Analog voltages and dedicated XADC input (0-1V range)
- Raw power input/3.3V regulated output
- QWIIC connector (shares pins on bank B)
- 100MHz oscillator
- 8 general purpose LEDs
- 1 button (typically used as reset)
- 256MB DDR3L @ 800Mb/s (400MHz)
- 32MBit Configuration FLASH
- FT2232HQ USB -> JTAG and USB -> UART (12Mbaud max)
- 5-12V input voltage on-board power supply
- 3.3V @ 4A (IO)
- 2.5V @ 500mA (triple voltage pins, derived from 3.3V)
- 1V @ 4A (VCCINT)
- 1.8V @ 1.2A (VCCAUX, triple voltage pins)
- 1.35V @1.2A (DDR3L)
- 1.8V @ 200mA (analog)
This device has been discontinued by the manufacturer in favor of the Au V2
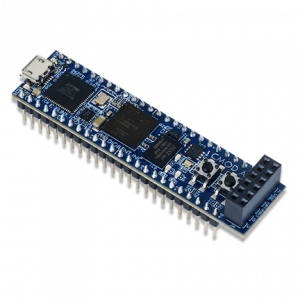
Digilent Cmod A7 is a development board based around the Xilinx Artix 7 FPGA. The Cmod, or Carrier Module, family of products is designed to offer quick, simple, and flexible integration of an FPGA into circuit design, prototyping, and learning/hobby projects.
The Digilent Cmod A7 is a small, 48-pin DIP form factor board built around a AMD® Artix®-7 FPGA that brings FPGA power and prototyping to a solderless breadboard.
The board includes a Quad-SPI flash for programming, as well as a USB-JTAG programming circuit and USB-UART bridge. The Cmod A7 also features a clock source, Pmod port, and onboard I/O with LEDs and pushbuttons. There are 44 FPGA I/O signals that are routed to 100-mil-spaced through-hole pins, making the Cmod A7 compatible with solderless breadboards. This form factor makes the Cmod A7 a great option for flexible and affordable prototyping, or learning FPGA and digital logic circuits. At just .7" by 2.75", it can also be loaded in a standard socket and used in embedded systems.
The Artix®-7 FPGA on the Cmod A7 provides the highest performance-per-watt fabric, transceiver line rates, DSP processing, and AMS integration for a cost-optimized FPGA. With the MicroBlaze Soft Processor Core from AMD, you can create embedded applications with a variety of peripherals, memory, and interfaces.
- System Features
- 512KB SRAM with an 8-bit bus and 8ns access times
- 4MB Quad-SPI Flash
- USB-JTAG Programming Circuitry
- Powered from USB or external 3.3-5.5V supply connected to DIP pins
- System Connectivity
- USB-UART bridge
- Interaction and Sensory Devices
- 2 LEDs
- 1 RGB LED
- 2 Push Buttons
- Expansion Connectors
- 48-pin DIP connector with 44 Digital I/O and 2 Analog inputs (0-3.3V)
- One Pmod connector with 8 Digital I/O
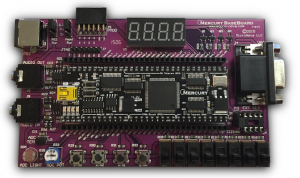
Micro Nova Mercury is a development board based around the Xilinx Spartan 6 FPGA.
- Xilinx Spartan-3A FPGA with 200K or 50K equiv. logic gates
- 50 MHz precision crystal oscillator
- 1 amp 1.2V and 3.3V voltage regulators
- USB and JTAG programmable
- 8 Mbit SPI Flash (up to 1.2Mb reserved for FPGA bitstream)
- Optional 4 Mbit external SRAM (512k x 8bit, 10ns)
- 8 channel 10-bit 200ksps ADC
- 30 GPIO pins with 5V tolerance and short-circuit protection
- 9 high-speed GPIO pins, 4 input-only pins
- 4 LEDs with GPIO pins, 1 user switch, 1 reset switch
- Friendly breadboard-compatible DIP 64 form-factor
This device has been discontinued by the manufacturer and its use is deprecated in the program.
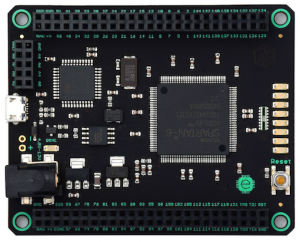
Alchitry Mojo is a development board based around the Xilinx Spartan 6 FPGA and the ATMega32U4 8-bit microcontroller. This device is the board used in the book "Learning FPGAs" by Justin Rajewski. It used by interns in the program to develop the IO devices for the calculator project.
The Mojo has an Arduino-compatible microcontroller whose main function is to program the FPGA over USB. However, once the FPGA is programmed, the microcontroller can be used as an ADC (eight analog inputs are broken out) and a USB-to-serial interface for your FPGA designs. Beyond the other bare necessities such as a 50 MHz oscillator, the Mojo features eight LEDs and a button (commonly used as a reset).
The I/O (a total of 84 digital I/O pins) on the Mojo is all at 3.3 V and is not 5 V tolerant. A level shifter was used at the junction between the FPGA and the 8085 microprocessor. Power can be supplied via the USB port, the barrel jack, the two holes, or the RAW input on the large headers. The supplied power should be between 4.8 V–12 V, with 5 V being the recommended voltage. You can connect an external power supply and the USB port at the same time, as the USB port is protected by a diode.
This device has been discontinued by the manufacturer and its use is deprecated in the program.